Example Applications
Localized inhibition of microtubule polymerization
RPOC can inhibit chemical processes at selected locations. For example, pairing with a photoswitchable inhibitor PST-1, RPOC can inhibit microtubule polymerization only in ER, or only in selected cells within a population, without affecting unwanted locations.
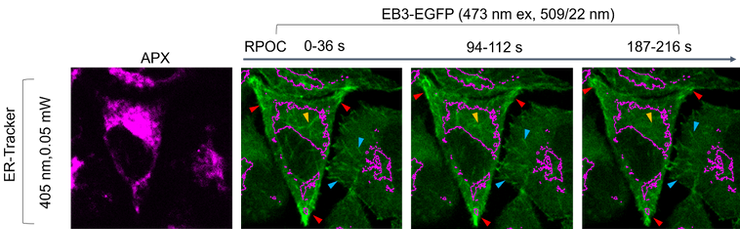


Dong, et al. Adv Sci, 2024, 2307342
Dong, et al. ACS Photonics, 12, 7, 3421-3434
Site-specific ROS generation
RPOC can generate ROS in selected organelles and quantify the laser dosage received by each cell. The dosage can be well correlated to cell responses. Lasers used for ROS generation include: 375 nm laser, 405 nm laser, and femtosecond NIR laser


Dong, et al. Adv Sci, 2024, 2307342
Ma, et al. Small Sci, 2025, 2500166
Single-organelle microsurgery
RPOC can perform single- or sub-organelle microsurgery without affecting unwanted locations.


Ma, et al. Small Sci, 2025, 2500166
Selective organelle perturbation and ROS generation
RPOC permits selective organelle perturbation using lasers and the generation of ROS solely in desired organelles. The interactive software allows to outline any cells. The signal-based APX selection permits automated target identification with optimal spatial precision. The generation of ROS in mitochondria induces leaking of MitoTracker into cytosol and oxidation of cellular EGFP.

Dong, et al. ACS Photonics, 12, 7, 3421-3434
Simultaneous treatment with different wavelengths
RPOC can simultaneously create different treatment conditions within the same field of view (FOV). This allows enhancement of the throughput and the study on how cells treated differently interact with each other. RPOC also enables fixed laser dosages for treatment of desired targets, or automatic stop of treatment after reaching a desired signal level. For example, it can photobleach fluorophores to any defined level and then automatically stop the photobleaching process.


Dong, et al. ACS Photonics, 12, 7, 3421-3434
Control of cell division
RPOC can control cell division and force cells to divide into the multi-nuclei form by perturbing centrosomes using a 405 nm laser. We can control the fate of cells after site-specific and chemical-specific optical control. The cell fate can be monitored in long-term to determine the impact of optical control.

Dong, et al. ACS Photonics, 12, 7, 3421-3434
Control chemical states in live cells
RPOC allows to site-specifically control states of photochromic molecules with submicron precision. As an example, a photoswitchable molecule cis−1,2-dicyano1,2-bis(2,4,5-trimethyl-3-thienyl)ethene (CMTE) is used.

Clark, et al. Nat Commun, 2022, 13, 4343
Raman activated cell-sorting
RPOC allows to perform Raman activated sorting of bacteria with high speed and specificity
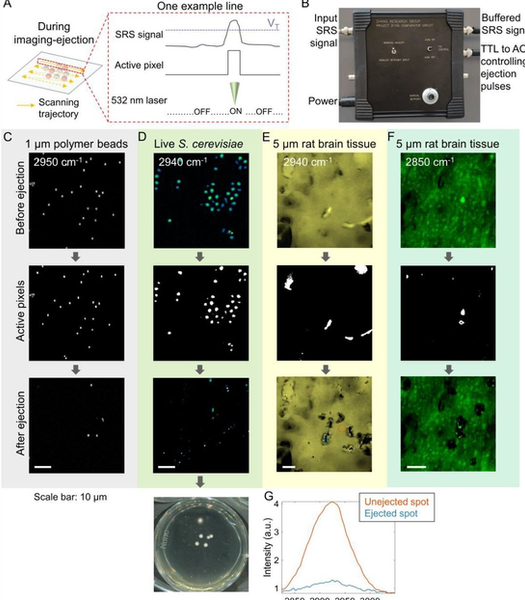
Zhang, et al. Sci Adv, 2024, 10, eadp2438
